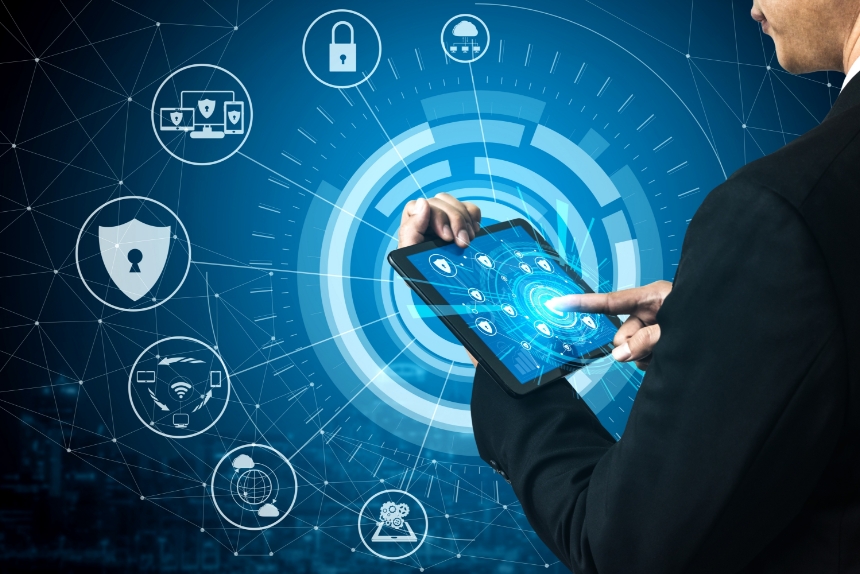
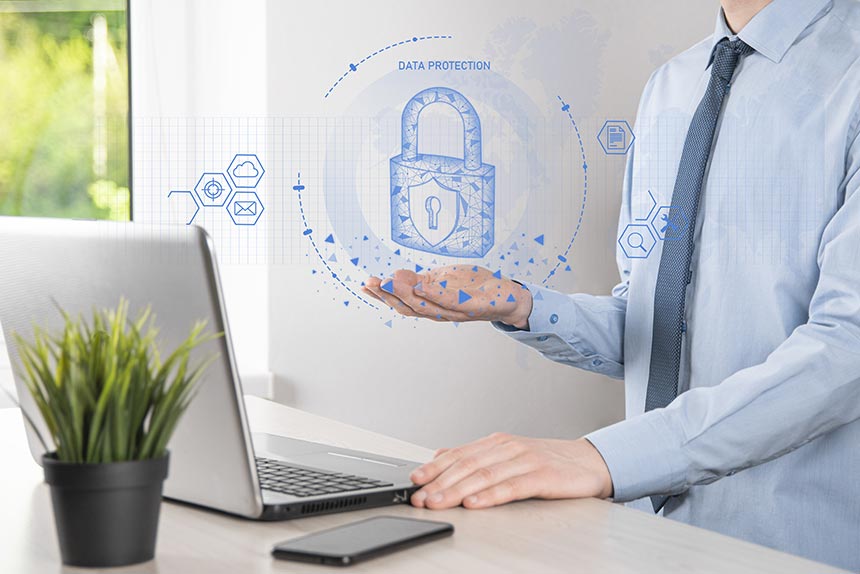
Transparency and Communication: Open communication about how data is used, how decisions are made, and how risks are managed builds confidence among stakeholders. Being honest and transparent, especially during challenging times, fosters trust.
Data Protection and Privacy: In the digital age, trust is increasingly linked to how well an organization secures its data. By investing in data protection measures, including encryption, secure storage, and robust cybersecurity policies, companies can reassure customers that their personal and sensitive information is in safe hands.
Ethical Business Practices: Trust is built through ethical decision-making. This means treating customers fairly, ensuring products and services meet quality standards, and operating transparently in all business dealings. Regular ethical audits and assessments can ensure a company’s values are consistently upheld.
Customer-Centric Culture: Trust is also about showing that you care about your customers’ needs. Offering excellent customer service, listening to feedback, and actively improving based on customer input reinforces the belief that you prioritize their well-being.
2. Ensuring Compliance: Navigating Legal and Regulatory Challenges
Compliance is a critical aspect of maintaining trust, especially in industries such as finance, healthcare, and technology, where organizations handle sensitive data and are subject to strict regulations. Regulatory requirements are constantly evolving, making it challenging for businesses to stay compliant.
Key Strategies to Ensure Compliance:
Stay Updated with Regulations: Compliance isn’t a one-time task. Laws and regulations evolve constantly, and companies must stay abreast of these changes. Regularly reviewing relevant laws, including privacy regulations like GDPR or industry-specific standards, ensures your organization remains compliant.
Implement a Compliance Framework: A comprehensive compliance management framework provides a roadmap for maintaining adherence to regulatory requirements. This framework should include clear policies, roles, and responsibilities related to compliance and establish processes for risk assessments, audits, and reporting.
Regular Audits and Assessments: Internal audits, risk assessments, and compliance reviews help identify gaps in compliance and mitigate risks before they lead to violations. These audits can identify areas where processes need improvement or where additional safeguards should be put in place.
Employee Training and Awareness: Training employees on compliance policies, industry regulations, and legal responsibilities ensures that everyone in the organization is aligned on the importance of maintaining compliance. Regular training sessions, along with ongoing awareness programs, will help reduce the risk of non-compliance.
Automate Compliance Processes: Compliance management tools can automate and streamline many aspects of the compliance process, such as tracking regulatory changes, managing audit trails, and generating compliance reports. This reduces the risk of human error and ensures that compliance tasks are completed efficiently.
3. Strengthening Governance: Ensuring Accountability and Oversight
Effective governance is crucial for ensuring that decisions are made in the best interest of stakeholders and in line with ethical standards. It helps guide an organization toward long-term success, ensuring that the company remains responsible, accountable, and aligned with its mission and values.
Key Strategies to Strengthen Governance:
Establish Clear Policies and Procedures: Governance begins with clear and well-communicated policies and procedures. These should cover everything from decision-making processes to risk management protocols. Ensuring consistency in how decisions are made and executed promotes accountability and transparency.
Board Oversight and Accountability: Strong governance includes having an active, engaged board of directors that provides oversight and strategic direction. Boards must hold management accountable for ensuring the organization complies with regulations, maintains ethical standards, and pursues sustainable growth.
Risk Management: An essential aspect of governance is identifying, managing, and mitigating risks. This includes operational, financial, reputational, and cybersecurity risks. A robust risk management strategy involves setting risk thresholds, regularly assessing vulnerabilities, and creating contingency plans to address potential crises.
Transparency in Decision-Making: Transparency ensures that decision-making processes are fair, accountable, and based on sound reasoning. By documenting decisions, justifying actions, and explaining why certain steps are taken, organizations create an environment of openness and trust with stakeholders.
Continuous Monitoring and Reporting: Governance requires ongoing monitoring of both operational and financial activities. Regular reporting of key performance indicators (KPIs) and compliance metrics ensures that senior management and the board can make informed decisions and stay on top of potential issues.
4. Integrating Trust, Compliance, and Governance: A Unified Approach
The best approach to enhancing trust, compliance, and governance is through an integrated strategy. These three elements must work in tandem to create a comprehensive framework for managing risks and meeting business objectives. By aligning compliance efforts with governance frameworks and prioritizing trust-building initiatives, organizations can create a solid foundation for long-term success.
Unified Governance Framework: Implement a unified governance structure that integrates compliance management, data protection, risk assessment, and trust-building practices into a cohesive strategy.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Ensure that compliance, governance, and security teams collaborate effectively. When these groups work together, they can identify overlapping concerns, streamline efforts, and build a cohesive approach to managing trust and compliance across the organization.
Continuous Improvement: Trust, compliance, and governance are not one-time efforts—they require continuous evaluation and improvement. Regular feedback loops, audits, and reviews ensure that these areas are consistently reinforced and aligned with evolving business and regulatory landscapes.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive and highly regulated environment, enhancing trust, ensuring compliance, and strengthening governance are fundamental to an organization’s reputation, legal standing, and long-term sustainability. By integrating these elements into a cohesive strategy, organizations can safeguard sensitive data, build strong customer relationships, and operate with integrity.
A commitment to transparency, ethical practices, and effective risk management not only reduces the likelihood of legal and reputational issues but also builds a strong foundation of trust that enables an organization to thrive. Whether you’re aiming to achieve regulatory compliance, enhance transparency, or build stakeholder confidence, prioritizing these three pillars will ensure that your business operates ethically, securely, and responsibly—today and in the future.